Financial insurance
Voluntary insurance against other financial losses
The voluntary insurance against other financial losses involves indemnity to the Insured of damages due to the loss of income, adverse natural phenomena, continuous, unforeseen expenses, loss of market value, failure (improper performance) of contractual obligations by the Insured’s counterparty and other damages as a result of the financial activities.
Insurance risks:
Financial losses of the insured occurred in the implementation of financial activities as a result of the following events (one or cumulative events):
1) loss of income by the Insured due to forced stop of the production process or reduction in its volume due to:
- loss (destruction) or damage to property;
- man-made disaster;
- extraordinary or insuperable circumstances;
- adverse natural phenomena;
- earthquake;
- hurricane, blizzard, storm, tornado;
- flood;
- tsunami;
- mudflow.
2) continuous costs:
- rent for premises, equipment or other property leased by the Insured in order to generate income from financial activities, if according to the terms of the lease, rental or other similar agreements, lease payments are payable by tenant regardless of damage to the leased property;
- taxes and charges payable regardless of the turnover and the financial results (property tax, land tax, etc.);
- interest on loans or other borrowed funds, if such funds were raised before the occurrence of an insurance event for investments in the area of work, which was interrupted due to the insurance event;
3) unforeseen expenses — expenses of the Insured to restore financial activity in the period of forced stop of the production process or reduction in its volume, i.e. costs suffered by the Insured to resume the interrupted activity as soon as possible in the amount that existed immediately before the loss;
4) loss of market value caused by:
- changes in market conditions;
- repair of the damaged property;
5) failed or improper performance of its obligations by the Counterparty under the civil contract as a result of:
- fire, explosion, accident (such events must have a cause-effect application to insurance event);
- force majeure;
- Counterparty’s bankruptcy, liquidation;
- acts of third parties (theft, robbery, hooliganism) fixed by court;
Insurance premium
The insurance premium is determined based on the size of insured sum and tariff rates.
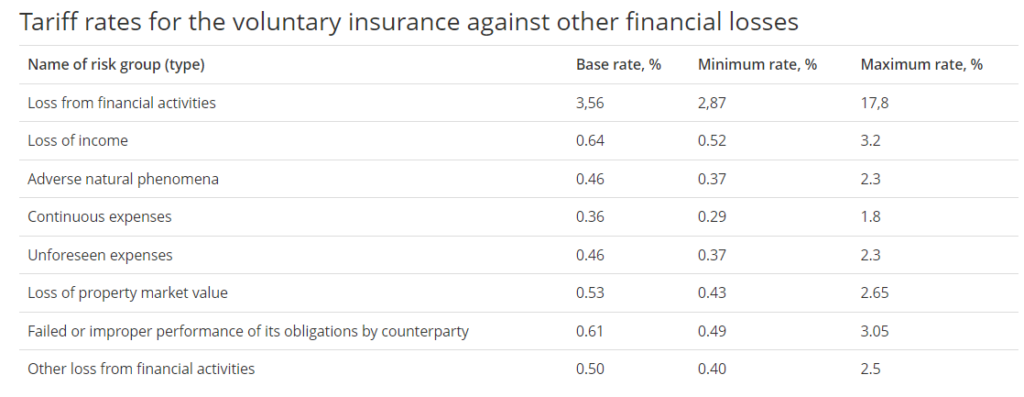
Tariff rates for the voluntary insurance against other financial losses
Tariff rate (premium) factors
The insurance premium is determined based on the size of insured sum and tariff rates.
Tariff rates for the voluntary insurance against other financial losses
| Name of risk group (type) | Base rate, % | Minimum rate, % | Maximum rate, % |
| Loss from financial activities | 3,56 | 2,87 | 17,8 |
| Loss of income | 0.64 | 0.52 | 3.2 |
| Adverse natural phenomena | 0.46 | 0.37 | 2.3 |
| Continuous expenses | 0.36 | 0.29 | 1.8 |
| Unforeseen expenses | 0.46 | 0.37 | 2.3 |
| Loss of property market value | 0.53 | 0.43 | 2.65 |
| Failed or improper performance of its obligations by counterparty | 0.61 | 0.49 | 3.05 |
| Other loss from financial activities | 0.50 | 0.40 | 2.5 |
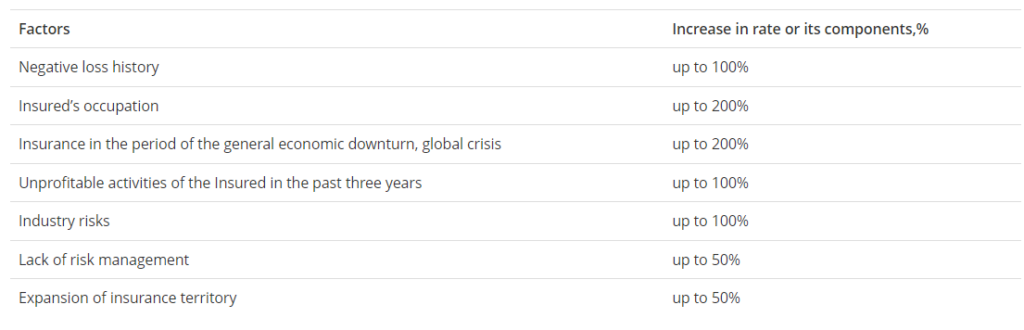
Tariff rate (premium) factors
| Factors | Increase in rate or its components,% |
| Negative loss history | up to 100% |
| Insured’s occupation | up to 200% |
| Insurance in the period of the general economic downturn, global crisis | up to 200% |
| Unprofitable activities of the Insured in the past three years | up to 100% |
| Industry risks | up to 100% |
| Lack of risk management | up to 50% |
| Expansion of insurance territory | up to 50% |
In general, the insurance rate can only be increased to 500%.
Deductible
Insurance contract specifies a deductible, which type and amount are determined by the agreement between the Parties and set either a percentage of the insured sum, or in absolute terms.